What are shuttle vectors?
Shuttle vectors are specifically designed for replication in different organisms or cell environments. These versatile vectors are characterized by their inclusion of multiple replication origins (oris) and a suite of selection markers, enabling them to operate efficiently across both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. They often incorporate tailored features: bacterial antibiotic resistance genes facilitate their selection in prokaryotic hosts, while eukaryotic selectable markers ensure precise identification in eukaryotic cells. This dual-functioning capability makes shuttle vectors an invaluable tool in genetic engineering and research.
What are the advantages of shuttle vectors over traditional vectors?
Versatility Across Systems
One of the most significant advantages of shuttle vectors is their versatility. Unlike conventional vectors that are limited to a single host system, shuttle vectors can be used in multiple organisms. This cross-compatibility makes them important for researchers working on projects that require gene transfer and expression across different biological systems. For instance, a shuttle vector can be used to clone a gene in a bacterial system for amplification and then transferred to a yeast or mammalian cell for expression analysis.
Efficient Gene Transfer
Shuttle vectors also offer enhanced efficiency in gene transfer. Their design incorporates optimized replication origins and selection markers that ensure high-efficiency replication and selection in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. This efficiency translates into higher transfection rates, reduced time for gene expression analysis, and improved overall productivity in research and biotechnology applications.
Facilitated Genetic Analysis
Shuttle vectors facilitate genetic analysis by allowing researchers to study gene function in different cellular contexts. For example, a gene cloned into a shuttle vector can be analyzed for its expression and function in a prokaryotic system first, providing preliminary data on its activity. Subsequently, the same vector can be used to study the gene's function in a more complex eukaryotic system, offering deeper insights into its biological role and potential applications.
Multiple Coning Sites
Shuttle vectors usually have multiple cloning sites, which can accommodate and stably carry exogenous genes or other genetic elements. This makes shuttle vectors more convenient for genetic engineering operations, allowing for easy gene insertion, deletion, replacement and other operations. In contrast, conventional vectors may be difficult to meet the needs of complex genetic engineering due to the limited number of cloning sites.
Streamlined Research Process
The use of shuttle vectors can streamline production pipelines in biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries. By enabling the seamless transfer of genetic material between different host systems, shuttle vectors facilitate the development of more efficient and cost-effective production processes. For example, in the production of therapeutic proteins, shuttle vectors can be used to clone and express the gene in a prokaryotic system for initial protein purification, followed by transfer to a eukaryotic system for post-translational modifications and final purification.
Efficient Screening and Identification
Shuttle vectors usually integrate multiple selection markers, including bacterial antibiotic resistance genes and eukaryotic selection markers, which enable the shuttle vectors to be easily screened and identified in the corresponding organisms. In contrast, conventional vectors may contain only a single selection marker, which is less efficient for screening and difficult to be applied in multiple organisms at the same time.
Gene Shuttle Vector | Synbio Technologies
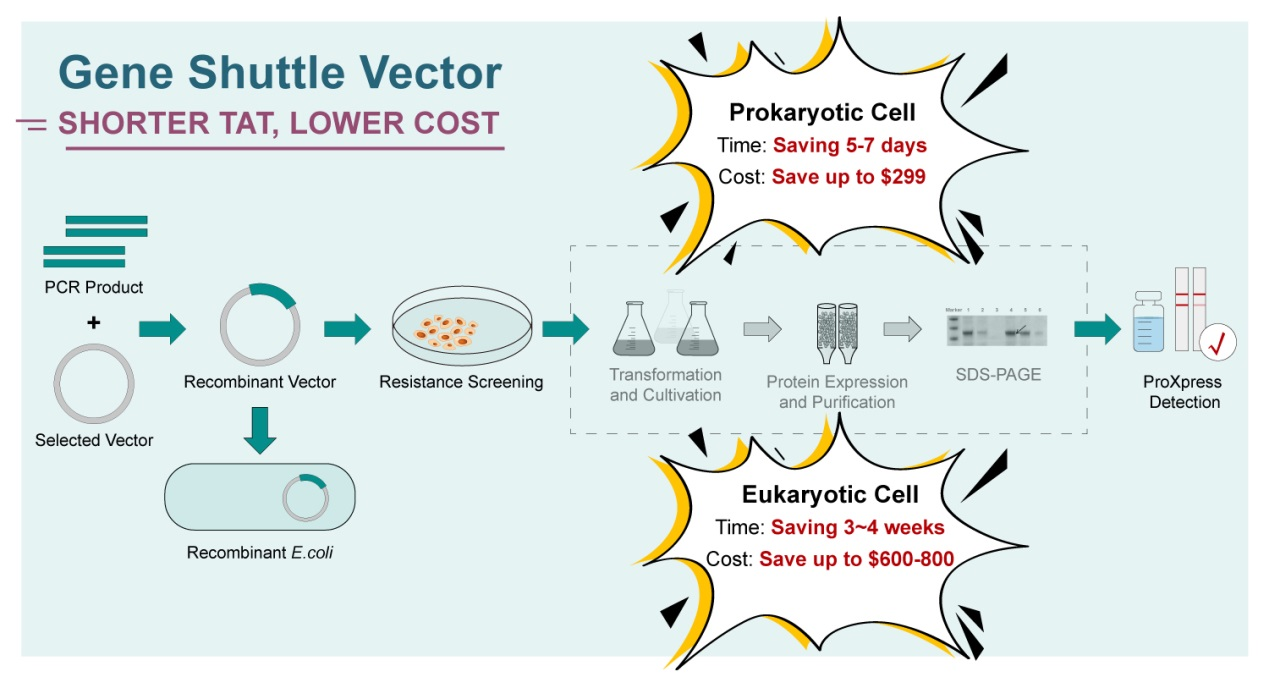
Synbio Technologies' gene shuttle vector designed for rapid protein expression detection. With our modified shuttle vector, protein expression detection can be conducted without the need for transformation operations. Compared to existing expression vectors in the market, our shuttle expression vector offers enhanced efficiency and reliability. By integrating the exclusive ProXpress technology, you can streamline your research process, enhancing efficiency and simultaneously cutting down your research costs.
References:
[1] Gnügge R, Rudolf F. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Shuttle vectors. Yeast. 2017 May;34(5):205-221.
 DNA Synthesis
DNA Synthesis Vector Selection
Vector Selection Molecular Biology
Molecular Biology Oligo Synthesis
Oligo Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA Synthesis Variant Libraries
Variant Libraries Genome KO Library
Genome KO Library Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools Virus Packaging
Virus Packaging Gene Editing
Gene Editing Protein Expression
Protein Expression Antibody Services
Antibody Services Peptide Services
Peptide Services DNA Data Storage
DNA Data Storage Standard Oligo
Standard Oligo Standard Genome KO Libraries
Standard Genome KO Libraries Standard Genome Editing Plasmid
Standard Genome Editing Plasmid ProXpress
ProXpress Protein Products
Protein Products