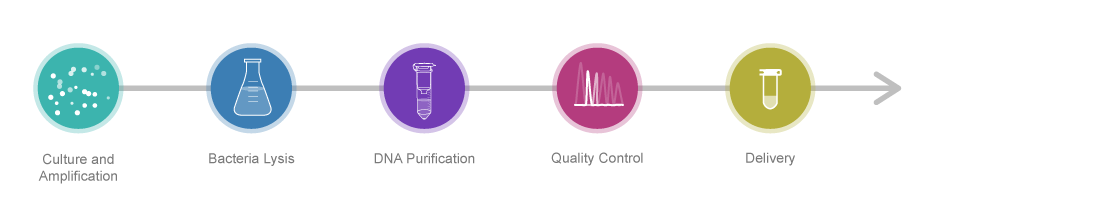
Plasmid DNA plays an important role in various scientific and industrial fields and is an essential tool for advances in gene therapy, diagnostics and drug development.
The major users of plasmid DNA services include researchers, R&D managers and professionals in the fields of gene therapy, in vitro diagnostics, biopharmaceuticals, industrial biotechnology and academic research.
Whether for gene therapy diagnostics, vaccine research or drug screening, plasmid DNA remains an indispensable tool for advancing medicine and science.
When it comes to plasmid DNA, proper handling is key to maintaining its integrity. Here’s how to best manage shipping and storage:
• Shipping Conditions
Plasmid DNA is typically dispatched in a 1x TE buffer solution. This method allows for safe transportation at room temperature conditions, ensuring that the plasmid remains stable throughout its journey.
• Short-term Storage
Temperature: For brief storage periods, up to two weeks, keep the plasmid at 4°C. This ensures the DNA remains stable without significantly impacting its functionality.
• Long-term Storage
Temperature Options: For extended preservation, choose to store plasmids at either -20°C or -80°C. Both temperatures offer excellent long-term protection against degradation.
Important Tip
Avoid Freeze-Thaw Cycles: Repeated freeze-thaw actions can degrade plasmid DNA. Try to minimize these cycles to retain the plasmid's quality. By adhering to these recommendations, you ensure that your plasmid DNA remains viable and ready for your next experiment or application.
 DNA Synthesis
DNA Synthesis Vector Selection
Vector Selection Molecular Biology
Molecular Biology Oligo Synthesis
Oligo Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA Synthesis Variant Libraries
Variant Libraries Genome KO Library
Genome KO Library Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools Virus Packaging
Virus Packaging Gene Editing
Gene Editing Protein Expression
Protein Expression Antibody Services
Antibody Services Peptide Services
Peptide Services DNA Data Storage
DNA Data Storage Standard Oligo
Standard Oligo Standard Genome KO Libraries
Standard Genome KO Libraries Standard Genome Editing Plasmid
Standard Genome Editing Plasmid ProXpress
ProXpress Protein Products
Protein Products