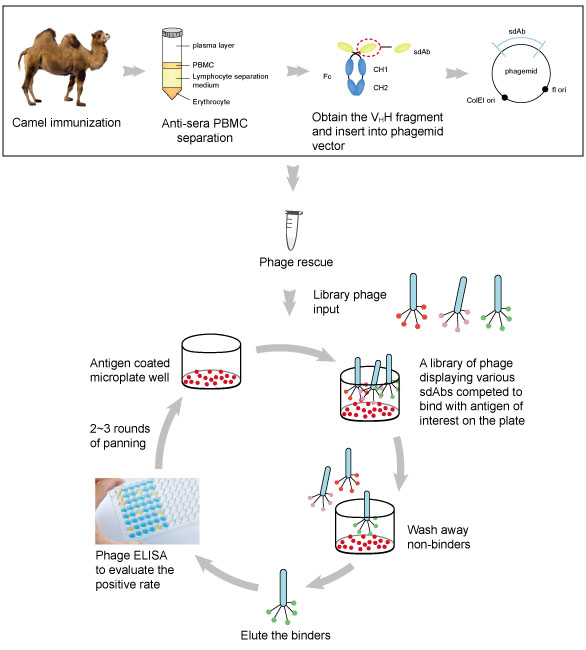
General Introduction of Single Domain Antibody(sdAb)
Recombinant antibodies, such as single domain antibodies (sdAb), represent the new generation of engineered antibody fragments. The presence of a single monomeric variable antibody domain reduces the size, raises stability, and increases solubility in comparison to conventional antibodies. Additionally, sdAbs offer not only enhanced permeability and reduced immunogenicity, but also straightforward and cost-effective production processes.
By leveraging Synbio Technologies’ extensive expertise and advanced sdAb discovery technology, we provide our customers with a comprehensive one-stop solution for antigen production and the specific expression of recombinant sdAbs.
Highlights
-
![]()
- Expert Antibody Production Team
-
![]()
- Proprietary Universal Antigen Immunization Technology
-
![]()
- Robust Phage-Display Technology Platform
-
![]()
- Advanced Yeast-Display Technology Platform (large library capacity: ~ 109)
-
![]()
- Cost-Effective
Service Details
|
Service Specifications
|
Turnaround Time
|
Camel immunization
(eg. dromedaries, camels, llamas, and alpacas)
|
10-11 Months
|
|
PBMC isolation and immune library construction
|
|
Screening of phage-displayed library
|
|
Functional assay for sdAb
|
Large scale yeast sdAb expression
(followed by properties identification)
|
Workflow
Deliverables
-
A glycerol stock of sdAb expressing bacteria (TG1)
-
Phage-displayed sdAb library
-
Top 5 identified sdAb strains and corresponding sequences
-
Full reports (PDF)
FAQs
Some common applications of sbABs include:
- Diagnostic tools and assays
- Therapeutic agents, particularly in oncology and infectious diseases
- Imaging agents for medical diagnostics
- Research tools for studying protein-protein interactions and cellular processes
sdABs are typically produced using recombinant DNA technology in microbial systems such as E. coli, yeast, or mammalian cell cultures. This allows for high yield and consistent quality.
Yes, sdAbs can be humanized to reduce their immunogenicity and improve compatibility with the human immune system, making them suitable for therapeutic applications in humans.
Resources
Get in Touch with Us
Related Services
 DNA Synthesis
DNA Synthesis Vector Selection
Vector Selection Molecular Biology
Molecular Biology Oligo Synthesis
Oligo Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA Synthesis Variant Libraries
Variant Libraries Genome KO Library
Genome KO Library Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools Virus Packaging
Virus Packaging Gene Editing
Gene Editing Protein Expression
Protein Expression Antibody Services
Antibody Services Peptide Services
Peptide Services DNA Data Storage
DNA Data Storage Standard Oligo
Standard Oligo Standard Genome KO Libraries
Standard Genome KO Libraries Standard Genome Editing Plasmid
Standard Genome Editing Plasmid ProXpress
ProXpress Protein Products
Protein Products