The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to Professor Victor Ambros of the University of Massachusetts Medical School and Professor Gary Ruvkun of Harvard Medical School, in recognition of their pioneering research on microRNA (miRNA) and its critical role in gene regulation.
-

Victor Ambros. Ill. Niklas Elmehed © Nobel Prize Outreach
-

Gary Ruvkun. Ill. Niklas Elmehed © Nobel Prize Outreach
Victor Ambros, born in 1953 in New Hampshire, earned his Ph.D. from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1979, where he also conducted postdoctoral research. He is currently the Silverman Professor of Natural Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Medical School.
Gary Ruvkun, born in 1952 in California, received his Ph.D. from Harvard University in 1982 and is now a professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School.
MicroRNAs are non-coding RNAs approximately 22 nucleotides long that regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally by pairing with target messenger RNAs (mRNAs). This mechanism plays a crucial role in biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and responses to external stimuli.
Ambros and Ruvkun's research began in the 1980s, during which they first identified the existence of miRNA in studies of development in the nematodeCaenorhabditis elegans. Although their early findings did not gain widespread attention, the importance of miRNA gradually became recognized following the discovery of let-7 in 2000, revealing its conservation and universality across different species.
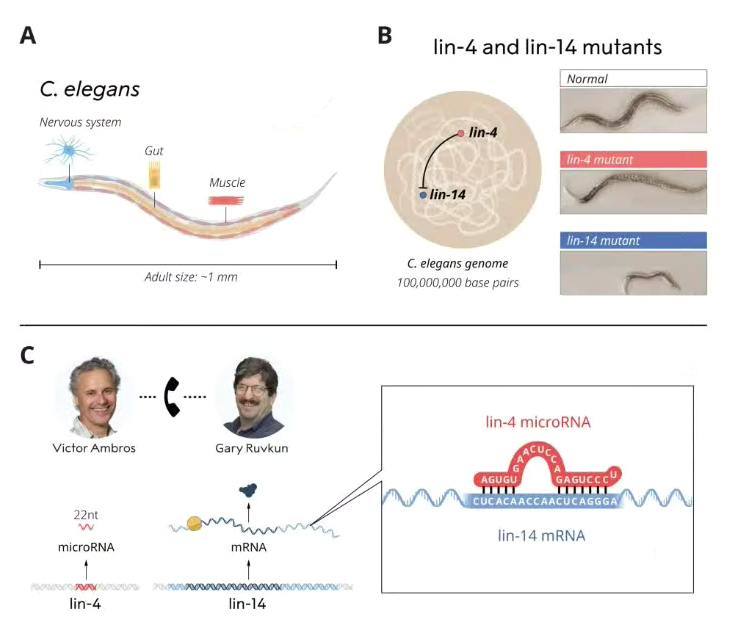
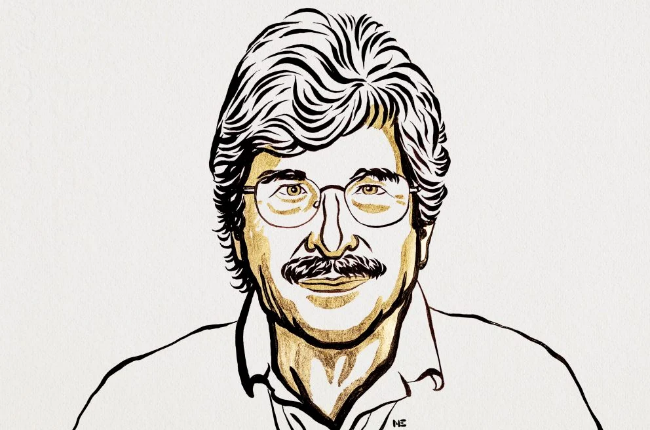
(A) C. elegans is a useful model organism for understanding how different cell types develop. (B) Ambros and Ruvkun studied the lin-4 and lin-14 mutants. Ambros had shown that lin-4 appeared to be a negative regulator of lin-14. (C) Ambros discovered that the lin-4 gene encoded a tiny RNA, microRNA, that did not code for a protein. Ruvkun cloned the lin-14 gene, and the two scientists realized that the lin-4 microRNA sequence matched a complementary sequence in the lin-14 mRNA. © The Nobel Committee for Physiology or Medicine. Ill. Mattias Karlén
To date, researchers have identified over 1,000 unique human miRNAs that regulate more than half of human genes. Dysregulation of miRNAs is associated with various diseases, including cancer, hearing loss, and bone disorders. They also play significant roles in embryonic development, cardiovascular health, and viral infections.
The Nobel Prize Committee stated: “The discoveries of Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun have fundamentally changed our understanding of gene expression regulation, laying an essential foundation for molecular biology and medical research.”
We extend our congratulations to these two outstanding scientists and look forward to their future research, which promises to bring further breakthroughs to the scientific community.
References:
1. Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843-854. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-y
2. Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75(5):855-862. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90530-4
3. Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kurodak MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Müller P, Spring J, Srinvasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature. 2000;408(6808):86-89. doi:10.1038/35040556
4. Zhang X, Zuo X, Yang B, Li Z, Xue Y, Zhou Y, Huang J, Zhao X, Zhou J, Yan Y, Zhang H, Guo P, Sun H, Guo L, Zhang Y, Fu XD. MicroRNA directly enhances mitochondrial translation during muscle differentiation. Cell. 2014 Jul 31;158(3):607-19.
5. Jeffries CD, Fried HM, Perkins DO. Nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of neural stem cell microRNAs. RNA. 2011 Apr;17(4):675-86.
6. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2024/press-release/
 DNA Synthesis
DNA Synthesis Vector Selection
Vector Selection Molecular Biology
Molecular Biology Oligo Synthesis
Oligo Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA Synthesis Variant Libraries
Variant Libraries Genome KO Library
Genome KO Library Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools Virus Packaging
Virus Packaging Gene Editing
Gene Editing Protein Expression
Protein Expression Antibody Services
Antibody Services Peptide Services
Peptide Services DNA Data Storage
DNA Data Storage Standard Oligo
Standard Oligo Standard Genome KO Libraries
Standard Genome KO Libraries Standard Genome Editing Plasmid
Standard Genome Editing Plasmid ProXpress
ProXpress Protein Products
Protein Products