Molecular cloning stands as a cornerstone technique in modern laboratories, pivotal for genetic research and applications. This technology allows researchers to recombine DNA fragments with vector DNA molecules in vitro, creating recombinant cloning vectors. These vectors are then introduced into host cells through transformation, facilitating the replication and amplification of the DNA fragments. Finally, vectors that meet the experimental criteria are selected for further study.
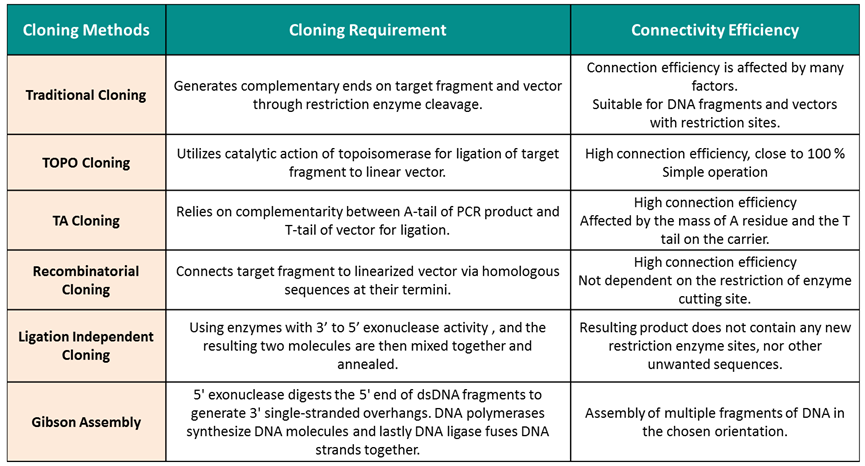
Comparative Analysis of Molecular Cloning Techniques
Process of Molecular Cloning
1. Vector Preparation
♦ Select an appropriate vector DNA, such as a plasmid or bacteriophage.
♦ Choose appropriate restriction enzyme (e.g.,EcoRI,HindIII) based on the vector’s restriction sites.
♦ Verify the linearized vector by agarose gel electrophoresis.
2. Preparation of Target Fragment
♦ Design and synthesize specific primers complementary to the sequences flanking the target gene.
♦ Mix template DNA, primers, dNTPs, buffer, and Taq polymerase in a PCR machine. Set up multiple temperature cycles to amplify the target gene.
3. Ligation of DNA Fragment to Vector
♦ Connect the linearized vector with the DNA fragment using DNA ligase to form a recombinant DNA molecule.
♦ Incubate at an appropriate temperature to allow the ligation reaction to proceed fully.
4. Transformation of Host Cells
♦ Introduce the recombinant DNA molecule into competent host cells (e.g., E.coli) via heat shock or electroporation.
♦ Spread the treated cells onto plates containing selective antibiotics.
5. Screening and Identification
♦ Screen forcolonies containing the target gene using antibiotic selection markers.
♦ Isolate individual colonies from the selective medium forfurther culture.
♦ Extract plasmid DNA and perform restriction digestion or sequencing analysis.
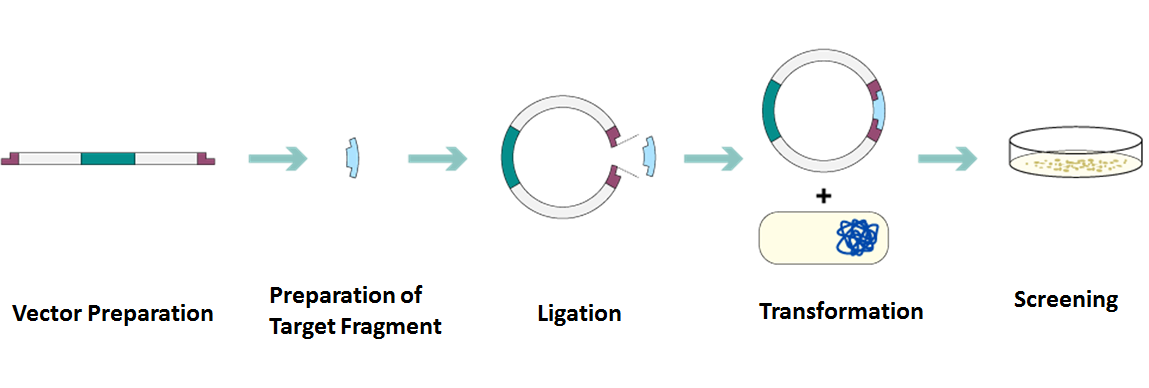
Molecular Cloning Workflow
Applications of Molecular Cloning
Molecular cloning has vast applications across various fields including gene engineering, biomedical research, and agriculture. It is instrumental in producing recombinant proteins, constructing gene libraries, studying gene functions, and advancing gene therapy. With ongoing developments in gene editing technologies, molecular cloning continues to evolve, accommodating more complex molecular manipulation needs.
Synbio Technologies | Advanced Molecular Cloning Solutions
As one of the leading biotech companies in the world, Synbio Technologies offers efficient and precise gene synthesis and molecular cloning services to scientists all over the globe. Our advanced gene synthesis platform perfectly synthesizes both complex and long DNA sequences. Our proprietary cloning technology allows for the insertion of DNA fragments into any desired vector site, bypassing the need for restriction sites, and caters to a wide range of cloning scenarios. Coupled with Sanger sequencing verification, we guarantee a rapid, error-free process from sequence design to molecular cloning, all at competitive prices.
References
[1] Lessard JC. Molecular cloning. Methods Enzymol. 2013;529:85-98.
[2] Watson JF, García-Nafría J. In vivo DNA assembly using common laboratory bacteria: A re-emerging tool to simplify molecular cloning. J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 18;294(42):15271-15281.
[3] Ashwini M, Murugan SB, Balamurugan S, Sathishkumar R. [Advances in Molecular Cloning]. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2016 Jan-Feb;50(1):3-9. Russian.
 DNA Synthesis
DNA Synthesis Vector Selection
Vector Selection Molecular Biology
Molecular Biology Oligo Synthesis
Oligo Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA Synthesis Variant Libraries
Variant Libraries Genome KO Library
Genome KO Library Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools Virus Packaging
Virus Packaging Gene Editing
Gene Editing Protein Expression
Protein Expression Antibody Services
Antibody Services Peptide Services
Peptide Services DNA Data Storage
DNA Data Storage Standard Oligo
Standard Oligo Standard Genome KO Libraries
Standard Genome KO Libraries Standard Genome Editing Plasmid
Standard Genome Editing Plasmid ProXpress
ProXpress Protein Products
Protein Products