Nucleic acid probes are a class of nucleic acid fragments that specifically recognize a target molecule (nucleic acid sequence) and are suitable for direct detection or known sequences with detectable markers. Nucleic acid probe technology is characterized by its specificity, sensitivity, speed and accuracy in determining specific gene sequences in nucleic acid samples.
|
Probes |
Detection Principle |
Advantage |
|---|---|---|
|
TaqMan |
The TaqMan probe is a dual-labeled hydrolysis probe, and when the probe is intact, the quenching group suppresses the fluorescent signal. During target amplification, the Taq enzyme cleaves the probe bound to the target sequence, which causes the fluorescent group to separate from the quenching group, releasing the fluorescent signal. |
1. Good specificity 2. reliable results 3. low cost 4. common probe types |
|
two-hybridization probe |
The donor and acceptor groups of a two-hybridization probe are on two probes, both of which can hybridize to the amplification product at different but very close positions. After hybridization the two groups are within 10 nm of each other (typically 1-5 bases). At this point the receptor groups fluoresce. |
Higher specificity than TaqMan |
|
molecular beacon probe |
Molecular beacons are TaqMan probe oligonucleotides with 5-6 complementary bases added to each of their junctions with the motifs to form a hairpin structure that brings the fluorescent motifs in close proximity to the quenching motifs and quenches the fluorescent signal. When the probe binds to the target sequence, the hairpin structure opens and the fluorescent group moves away from the quenching group, resulting in a fluorescent signal.
|
Higher specificity, ideal probe for genetic screening, SNP detection and diagnostic assays for pharmacogenetic applications |
|
MGB probe |
MGB (minor groove binding group) probes, like TaqMan probes, have a fluorescent group and a quenching group at each end. The difference is that there is an MGB near the quenching motif, and in case the probe does not bind the target sequence, the MGB probe randomly coils to bring the fluorescent motifs in close proximity. When the probe binds the target sequence, the MGB helps to linearize the probe and the fluorescent group glows. |
Binding of MGB increases the Tm value of the probe, increasing the specificity of the hybridization reaction and improving the sensitivity of the assay.MGB probes are suitable for the detection of single-base mutations (SNP typing).
|
|
Scorpion-shaped probe |
The scorpion probe differs in that it carries a sequence that matches a region downstream of the primer binding site and within the amplicon, and its 3' end is linked to the PCR primer by a PCR blocker.The product obtained by PCR and the scorpion probe are one molecule, and hybridization of the probe is within the molecule without the involvement of two molecules, resulting in a more rapid and efficient hybridization reaction. |
Applicable to a wide range of nucleic acid detection fields. For example, gene mutation detection, viral RNA/DNA detection and cellular diagnostics. |
|
Dual quenching probe |
Dual quenching probes differ from normal probes by the addition of a second quenching group inside the probe. As the length of the probe increases, the quenching effect of the single-quenching probe deteriorates, and the double-quenching probe has been developed. The internal quenching group reduces the fluorescence “leakage” and results in lower fluorescence background signals in experiments. |
Suitable for replacing common probes with lengths greater than 25 nt, or for qPCR assays with high background signals
|
|
LNA probe |
LNA (Locked Nucleic Acid) is a class of modified nucleotides that have been modified to contain methylene bridges, which are capable of restricting the flexibility of ribose structure. Because LNA and DNA/RNA have the same phosphate backbone in structure, it has good recognition ability and strong affinity for DNA and RNA. |
The addition of LNA to the probe sequence improves the specificity of the probe, facilitates the use of shorter qPCR probes, and is suitable for some specialized sequences
|
qPCR probes Application
Gene Expression Analysis: qPCR probes serve as precise tools for measuring either the relative or absolute expression levels of specific genes across various samples. This technique facilitates a deep understanding of gene regulation, the identification of biomarkers, and the comparative analysis of gene expression under diverse experimental scenarios (such as treatments versus controls).
Pathogen Detection and Quantification: Utilizing qPCR probes allows for the sensitive and swift detection and quantification of DNA or RNA from pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi. This capability is invaluable for clinical sample analysis, environmental monitoring, and food safety testing, ensuring rapid identification of infectious agents.
Genetic Mutation Detection: qPCR probes can be tailored to detect specific genetic mutations or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), providing a targeted approach to genetic analysis.
Quantification of DNA/RNA Targets: These probes are also employed to quantify the precise amounts of specific DNA or RNA in a sample, encompassing viral load measurement, gene copy number variations, and microbial load quantification.
Environmental and Food Safety Testing: In the realms of environmental science and food safety, qPCR probes are indispensable for detecting specific microbial contaminants or pathogens. This technology aids in the monitoring of water quality, assessment of soil health, and the detection of pathogens in food products, ensuring the safety and integrity of our ecosystems and food supply.
Cellular and Developmental Biology: qPCR probes play a pivotal role in studying gene expression during cellular differentiation, development, or in response to external stimuli. By leveraging this technology, researchers can gain insights into the molecular mechanisms that underlie developmental processes, cell fate determination, and responses to various stimuli.
Synbio Technologies |Diagnosis Probe Services
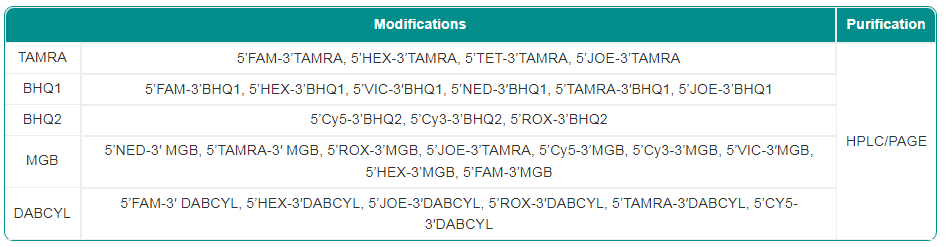
Synbio Technologies provides high quality nucleic acid probes with batch-to-batch consistency for qPCR/SNP detection. Our probes can also be labeled at the 5′ and 3′ ends of a designated position according to the specific needs of our customers. Depending on your project, we can modify these probes in order to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and diversity of qPCR assays.
Service Detail
 DNA Synthesis
DNA Synthesis Vector Selection
Vector Selection Molecular Biology
Molecular Biology Oligo Synthesis
Oligo Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA Synthesis Variant Libraries
Variant Libraries Genome KO Library
Genome KO Library Oligo Pools
Oligo Pools Virus Packaging
Virus Packaging Gene Editing
Gene Editing Protein Expression
Protein Expression Antibody Services
Antibody Services Peptide Services
Peptide Services DNA Data Storage
DNA Data Storage Standard Oligo
Standard Oligo Standard Genome KO Libraries
Standard Genome KO Libraries Standard Genome Editing Plasmid
Standard Genome Editing Plasmid ProXpress
ProXpress Protein Products
Protein Products