Synbio Technologies provides a broad range of DNA technologies for antibody discovery services. Our technical platforms span all stages of antibody discovery by integrating antibody genes sequence, de novo antibody design, antibody humanization, antibody genes synthesis, recombinant antibody expression, monoclonal antibody preparation and polyclonal antibody preparation. We aim to use our high-quality products and cost-effective solutions to support the development of biobased medicines within academia, biotechnology, and pharmaceutical industries.
Case Studies
i. Algorithm guided antibody design of an antibody
Here we used a computational method to aid the de novo design of PXX antibody: The PXX structure was first modeled using a homology-based modeling method. We extracted the frameworks and complementary determinant regions (CDRs) from antibody structures. Using frameworks as templates, we assembled CDRs onto the frameworks to construct an antibody library, and the antibody structures were modeled from their homologous protein structures. Then, the antibodies were docked onto the antigen and ranked according to the interaction energy. A certain number of best antibody hits were selected and the antibody sequences were synthesized and screened to get potential antibodies.
PXX is an important negative immunoregulatory factor that was expressed by tumor cells and reduces the body’s immune response. Antibodies that bind to PXX and block its signaling pathway can be used as therapeutics for the treatment of carcinoma. In this case, our designed PXX antibody achieved an affinity of 10-11 M, which provided a novel anti-PXX antibody and candidate drugs. The time period and cost for antibody discovery were greatly reduced using this computational designing method.
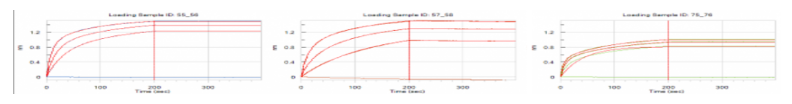
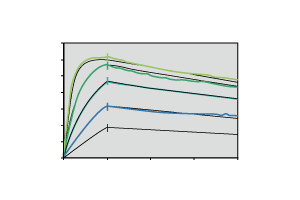
Figure 1. Kd measurement by protein A based capture approach
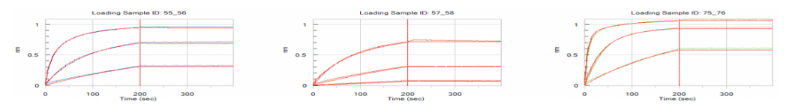
Figure 2. Kd measurement by anti-human Fc based capture approach
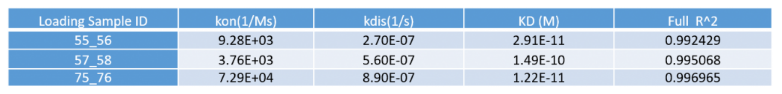
Figure 3. Kd values of the antibody samples
ii. Antibody library construction for a target protein
For protein CXX, we implemented a novel approach to construct antibody library: We extracted the frameworks and complementary determinant regions (CDRs) were extract from antibody structures and sequences. Using frameworks as templates, we assembled CDRs onto the frameworks to construct an antibody library, and the antibody structures were modeled from their homologous protein structures. The antibodies were docked onto the CXX protein and ranked according to the interaction energy. We then constructed an antibody library with around 106 antibody sequences according to the results. These sequences were synthesized and screened. The functionally active molecules were then obtained for further research.
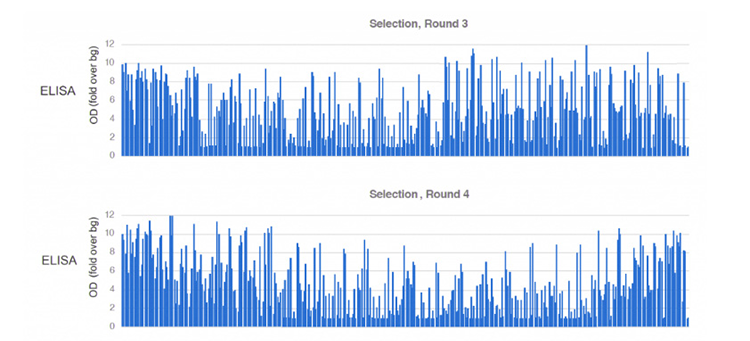
Figure 4. Round 3 & Round 4 ELISA screening of the antibody candidates
iii. Antibody discovery through bioinformatics analysis for Z virus infection
Blood samples were collected on the 6th and 13th day after Z virus infection. The antibody repertoire was sequenced. The NGS data was analyzed and clustered to get germline and CDR information. By comparing the results from two samples, we were able to select the top 50 differentially expressed antibodies. Then, the antibody genes were synthesized, expressed, and characterized in HEK cells. The active antibody to Z virus was screened using immune repertoire sequencing method.
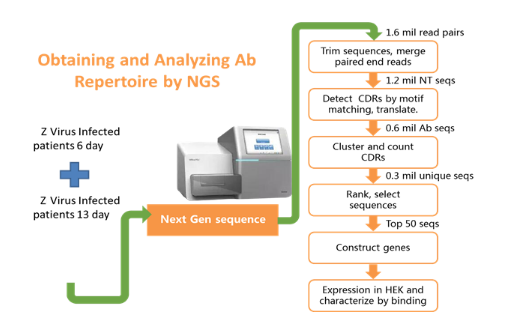
Figure 5. The workflow of obtaining the viable antibodies against Z virus