Metabolomics reflects static metabolite abundance, and the increase of a single metabolite may be due to either the activation of the synthetic pathway or the inhibition of the consumption pathway. Therefore, Metabolomics is often not enough to explain all the problems in the study of specific metabolic pathways and metabolic networks. As a complementary tool to metabolomics, Metabolic Flux Analysis (MFA) uses stable isotopes (13C or 15N) to label specific molecules and track their metabolic processes in an organism to obtain dynamic information about metabolites in metabolic pathways. MFA is the only tool that can quantify energy flows (i.e., ATP, cofactor generation and consumption) and their balances.
Applications
- Medical Research: Tumor metabolism mechanism, immune related diseases, metabolic diseases, stem cell development and differentiation, etc.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Simulate physiological processes of biology, bacterial metabolites, stress resistance, commercial crop quality, breeding, animal nutrition, meat quality, etc.
Competitive Advantages
- Advanced Instrument Platform: Orbitrap LC-MS & UHPLC-QQQ-MS & GC-Q-MS.
- Personalized Service: Professional bioinformatics teams & personalized bioinformatics analysis services.
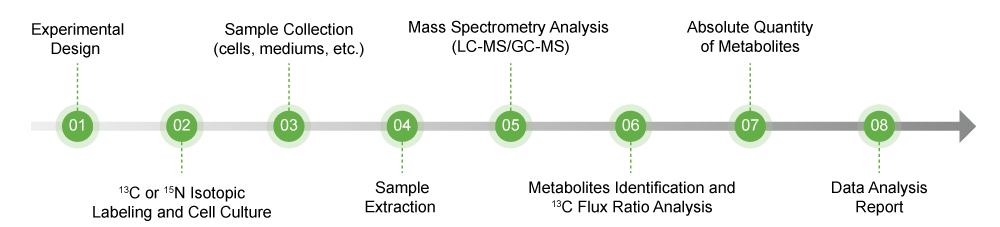
MFA Work Flow
Service Specifications
Service Specifications
| Service Types | Sample Requirements | Platform | Price | Turnaround Time | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis Flux Ratio |
|
|
Inquire | Inquire |
|
| TCA Pathways Flux | |||||
| Pentose Phosphate Pathways |
Analysis Item
| Number | Analysis Item | Number | Analysis Item |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raw data preprocessing | 5 | 13C flux ratio differential analysis |
| 2 | Isotopic distribution of metabolites | 6 | Hierarchical cluster analysis |
| 3 | Identification of metabolic pathways | 7 | PCA analysis |
| 4 | 13C flux ratio analysis |
Data Analysis
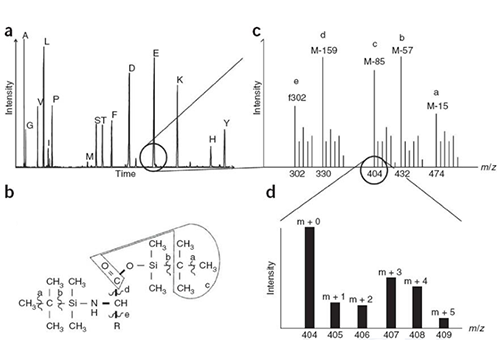
Isotopic Information of Metabolites
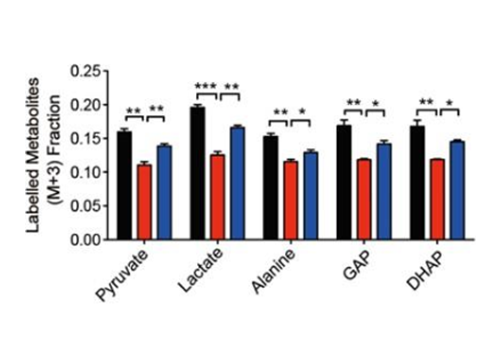
13C Flux Ratio Differential Analysis
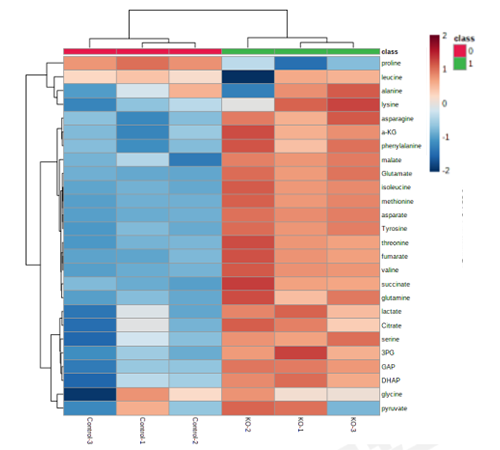
Hierarchical Cluster Analysis
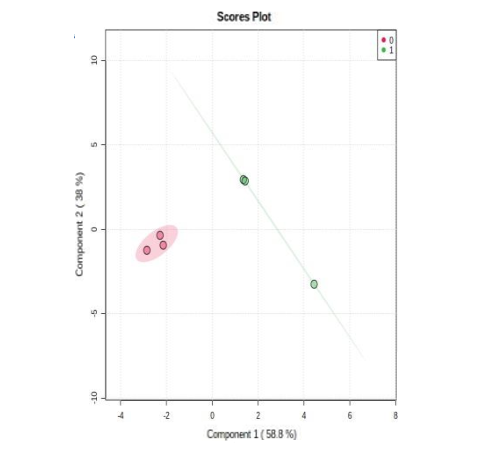
PCA Analysis

