Synbio Technologies’ proprietary Syno®2.0 gene synthesis process includes computational design of short oligos, which can then be reliably synthesized, assembled, and cloned into the desired vector. An available precursor to this process is optimization of the gene sequence for improved protein expression and other purposes.
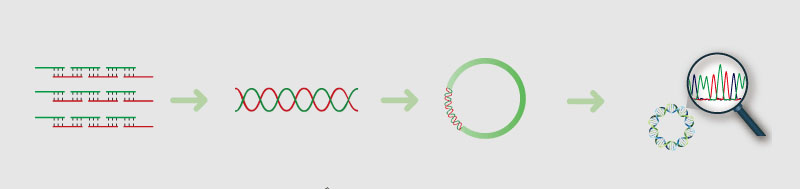
Fig. 1 Syno®2.0 gene synthesis process
A large number of oligos can be synthesized in parallel on gene chips. The Syno®3.0 next generation DNA synthesis platform offers revolutionary large-scale gene synthesis in an efficient, low cost manner that will open up new avenues for the development and industrialization of synthetic biology applications.
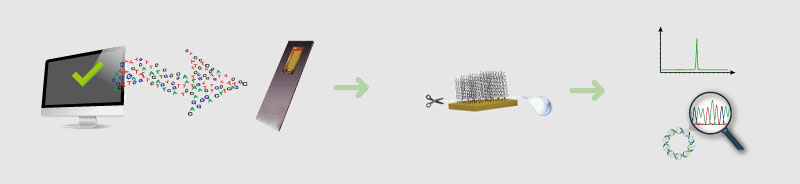
Fig. 2 Syno®3.0 gene synthesis process
Gene synthesis process–Codon Optimization:
Codon optimization refers to the use of preferred codons – that is, to avoid the usage of rare codons with low utilization – to simplify secondary structure of mRNA after gene transcription. It also involves the replacement of motifs that hinder efficient expression with those that promote it, as well as the adjusting of GC content and other factors in order to optimize gene expression.
Learn more about Codon Optimization:(click here to learn more:codon optimization)
- Codon Usage Bias
- Synbio Technologies’s NGTMCodon Optimization Software
- Synbio Technologies’s Codon Optimization Strategy
Gene synthesis process–Oligo Synthesis:
Syno®2.0 gene synthesis technology:
- Higher flexibility
- Less cost effective
- Limited throughput
Syno®3.0 gene synthesis technology:
- Lower price (starting from $0.09/bp)
- High throughput (synthesis of over 500,000 nucleobases and building DNA strands as long as 30,000bp on a single chip)
- Limited flexibility
Learn more about Synbio Technologies’ Synotype platform
- Synotype platform
- Syno®2.0 gene synthesis
- Syno®3.0 gene synthesis
Gene synthesis process—Gene Assembly:
Comparison of popular DNA assembly technologies:
| Projects | Gibson Assembly | Yeast Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| DNA polymerase/Taq ligase | Need | No need Yeast has homologous recombination capability |
| Multiple fragment | One-time assembly | One-step assembly |
| Large DNA fragment/Genome | < 20K base pairs | Up to 1.08M base pairs |

